Make your WordPress website look amazing with the Hover Card block from the Nexter Blocks. This block lets you design eye-catching and interactive content layouts. You can present your content in a fresh and engaging way, grabbing your visitors’ attention and giving them a fantastic experience on your site.
Required Setup
- Make sure the default WordPress Block editor is active.
- You need to have the Nexter Blocks plugin installed and activated.
- Make sure the Hover Card block is activated, to verify this visit Nexter → Blocks → and Search for Hover Card and activate.
How to activate the Hover Card Block?
Go to
- Nexter → Blocks
- Search the block name and turn on the toggle.

Key Features
- Custom Content Layout – You can easily create a custom content layout.
- Different Content Type – You can use different types of content like text, image, and HTML.
How to Use the Hover Card Block?
Add the Hover Card block on the page.
Then click on the Design from Scratch button to design the layout from scratch.
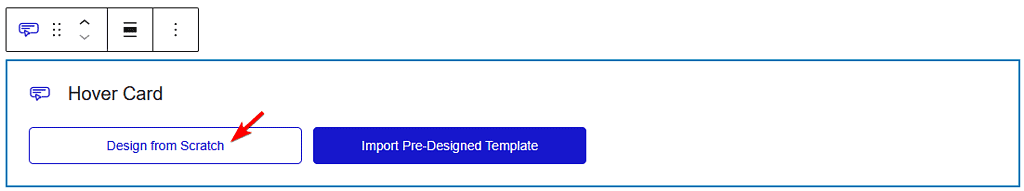
Note: By clicking on the Import Pre-Designed Template button, you can import a preset template and customize it as per your requirements.
Note: This block is for developers only, it requires a good understanding of HTML and CSS to make custom layouts.
Note: Because this block has so many customization options, it can load a bit slowly at first (*only in the editor). Once loaded, it will work smoothly like any other block.
This is a repeater type block, so you’ll find one repeater item by default, in the Code Structure section open it.
From the Open Tag dropdown, under the Open tab, you have to select the opening tag. Here you’ll find multiple tag options –
Div – This is to open a div tag.
Span – This is to open a span tag.
H1 – This is to open a h1 tag.
H2 – This is to open a h2 tag.
H3 – This is to open a h3 tag.
H4 – This is to open a h4 tag.
H5 – This is to open a h5 tag.
H6 – This is to open a h6 tag.
a – This is to open a tag.
p – This is to open a p tag.
None – This option won’t open any tag. You can use this option to add HTML content where no tag is required. If a tag is not closed within the item with this option, it can be used to add multiple elements inside one element.
For the a tag only, you’ll get a URL field where you can add a URL for the anchor tag.
In the Class Name field, you can add a CSS class name for a tag (except for the None option). This class can be used to target the element for styling.
Note: Make sure to add the class name without .(dot) in front.
From the Close Tag dropdown under the Close tab, you have to select the closing tag.
Default – This will auto close the tag opened in the Open tab.
For Div, Span, H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, H6, p and a options it will close the respective tags.
None – This option will not close the tag opened in the Open tab. This can allow you to add multiple elements inside one element.
Then from the Content section, you have to select the content type. Here you’ll find different content types –
None – With this option, no content will be added. This can be used to create an empty container that can have other containers in it without its own content.
Note: If Open Tag and Content both are set to None then you won’t see any options.
Text – With this option, you can add text content in the selected tag.
Image – With this option, you can add image content in the selected tag.
HTML – With this option, you can add HTML content to the selected tag.
With each content type (except None) you’ll get relevant options.
Note: When the open tag is set as None, the style options will not be available.
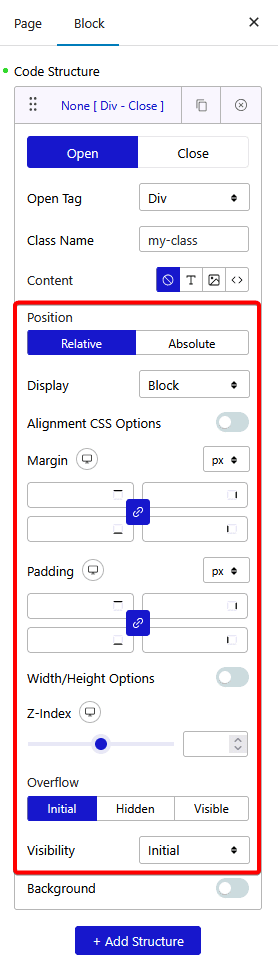
Position – From here, you can set the position to Relative or Absolute.
Display – From here, you can set the display property to Block, Inline Block, Flex, Inline Flex, Initial and Inherit for the element.
Note: Based on the selected display property, you’ll see additional styling options.
Alignment CSS Options – From here, you can set the text alignment by turning on the toggle. For Flex and Inline Flex display property, you’ll get some flex alignment related options.
Note: The Text alignment option will depend on the display property set in the Display dropdown.
Margin – From here, you can add margin to the element for different devices.
Padding – From here, you can add padding to the element for different devices.
Left – You’ll see this option when the position is set to Absolute. From here, you can set the left offset.
Right – You’ll see this option when the position is set to Absolute. From here, you can set the right offset.
Top – You’ll see this option when the position is set to Absolute. From here, you can set the top offset.
Bottom – You’ll see this option when the position is set to Absolute. From here, you can set the bottom offset.
Width/Height Options – From here, you can set the width and height of the element.
Z-Index – From here, you can set the z-index value of the element for different devices.
Overflow – From here, you can set the overflow property of the element.
Visibility – From here, you can set the visibility property of the element.
By enabling the Background toggle, you can set the background style of the element for both normal and hover state.
Note: When the open tag is set as None, the background style option will not be available.
Normal tab –
- Background – From here, you can set the background.
- Border – From here, you can set the border.
- Border Radius – From here, you can set the border radius of the element for different devices.
- Box Shadow – From here, you can set the box shadow.
- Transition CSS – Here you can manually add CSS transition value to the element.
- Transform CSS – Here you can manually add CSS transform value to the element.
- Opacity – From here you can add opacity to the element.
Hover tab –
- Custom Hover – By enabling this toggle, you can add a class name to the parent container of the element. On hovering that parent container, the CSS property set in the Hover tab of the current element will be applied.
Note: Make sure to add the class name without .(dot) in front.
The rest of the options are the same as in the Normal tab, the values you set here will apply on hover only.
Depending on the content type selected in the Content section, you’ll get some extra styling options for that specific content type.
Click on the +Add Structure button to add multiple elements.
Following this process you can create a custom layout with the Hover Card widget.
After creating the structure, you can click on the Render HTML button at the top to see the output in the editor.

Advanced options remain common for all our blocks, you can explore all it options from here.